In today's interconnected world, computer networks play a vital role in our daily lives, from the internet we browse to the emails we send and the files we share. But what exactly is a computer network, and how does it work? In this blog post, we'll explore the basics of computer networks to help you gain a better understanding of this essential technology.
What is a Computer Network?
At its core, a computer network is a collection of interconnected computers and devices that can communicate with each other. These networks can vary in size, ranging from a small home network connecting a few devices to massive global networks like the internet, linking billions of devices worldwide.
Components of a Computer Network:
-
Nodes: Nodes are the individual devices or computers connected to the network. These can include desktop computers, laptops, smartphones, servers, and even IoT devices like smart thermostats or cameras.
-
Links: Links are the connections between nodes, and they can take various forms. In wired networks, such as Ethernet, links are physical cables, while wireless networks use radio waves to establish connections.
-
Router: A router is a critical component in many networks, as it directs data traffic between different nodes and networks. It ensures that data packets find the most efficient path to their destination.
-
Switch: A network switch is used to connect multiple devices within a local area network (LAN). It allows devices to communicate directly with one another, increasing efficiency and reducing network congestion.
-
Protocols: Protocols are a set of rules and conventions that govern how data is transmitted and received in a network. Common network protocols include TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), which is the foundation of the internet, and HTTP/HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol/Secure), used for web communication.
Types of Computer Networks:
-
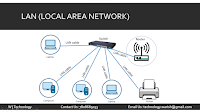
LAN (Local Area Network): LANs are typically small networks confined to a single location, like a home, office, or school. They are often used for sharing resources like printers or internet connections.Local Area Network (LAN)
-
WAN (Wide Area Network): WANs cover a broader geographic area and connect multiple LANs. The internet itself is a massive WAN that connects devices and networks worldwide.Wide Area Network (WAN) -
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network): MANs cover a city or a large campus, offering high-speed connectivity to multiple locations within a metropolitan area.Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
How Computer Networks Work:
Computer networks function by transmitting data in the form of packets. When you send an email or visit a website, the data is broken down into packets, each with a destination address. These packets travel through the network, passing through routers, switches, and various other network devices until they reach their destination. Once there, they are reassembled into the original data.
Security in Computer Networks:
Network security is crucial to protect data and prevent unauthorized access. Firewalls, encryption, and authentication mechanisms are commonly used to safeguard networks and the information they carry.
In conclusion, computer networks are the backbone of our modern digital world, enabling communication and data exchange on an unprecedented scale. Understanding the basics of computer networks can help you navigate the digital landscape more effectively and appreciate the complexity that makes our interconnected world possible. Whether you're setting up a home network or exploring a career in IT, this foundational knowledge is a valuable asset.


















0 Comments