Python Dictionaries: A Complete Guide for Beginners
Python dictionaries allow developers to store and manage data in a key-value pair format, making them essential for efficient data manipulation.
What is a Python Dictionary?
A Python dictionary is an unordered, mutable, and indexed collection of key-value pairs.
As of Python version 3.7, dictionaries are ordered. In Python 3.6 and earlier, dictionaries are unordered.
Creating a Dictionary
student = {
"name": "John Doe",
"age": 20,
"course": "Computer Science"
}
device = dict(brand="Apple", model="iPhone 13", price=999)Accessing Dictionary Elements
print(student["name"]) # Output: John Doe
print(device.get("brand")) # Output: AppleModifying a Dictionary
student["age"] = 21
student["grade"] = "A"
device.pop("price")Dictionary Methods
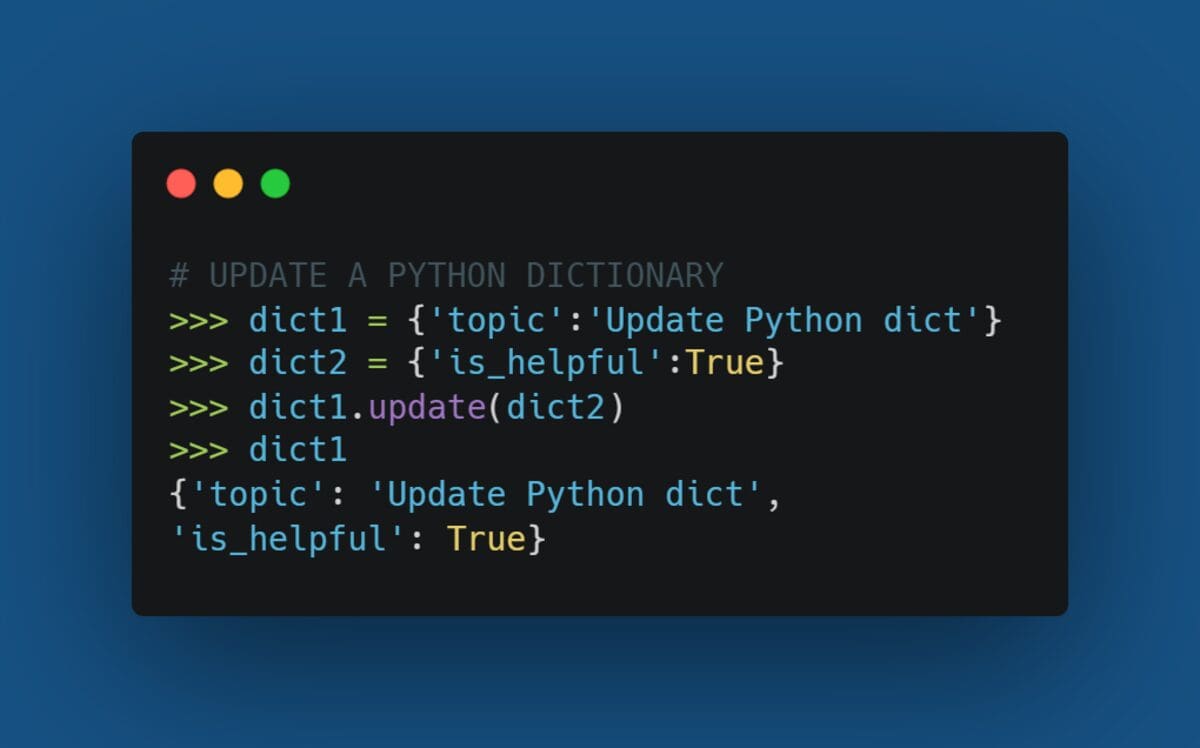
keys()– Returns a list of keys.values()– Returns a list of values.items()– Returns a list of key-value pairs.update()– Merges another dictionary into the existing one.pop()– Removes an item based on the key.
print(student.keys())
print(student.values())Dictionary Comprehension
squares = {x: x*x for x in range(1, 6)}
print(squares)Use Cases of Dictionaries
- Storing configurations in applications.
- Caching and memoization for performance optimization.
- Representing JSON data in APIs.
- Grouping and counting occurrences in datasets.
Conclusion
Python dictionaries are an indispensable tool for developers, offering efficiency, flexibility, and ease of use.
Copied to clipboard!











0 Comments