Recap of OSI Model
As we all know that the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual framework that standardizes the functions of a telecommunication or computing system into seven abstraction layers. As : Physical Layer, Data Link Layer, Network Layer, Transport Layer, Session Layer, Presentation Layer & Application Layer. Each layer represents a specific aspect of network communication, and the model is designed to facilitate interoperability between different systems and devices.Networking Device & Data Flow
Network devices play a crucial role in the efficient flow of data within a computer network. These devices act as the building blocks that enable communication, connectivity, and data transfer among various nodes in the network. Here's a brief note introducing the concept of network devices and highlighting their importance in data flow.
In our complex world of connected devices, hidden tools called network devices work tirelessly to move information smoothly across the internet, like silent heroes behind the scenes. Like : Routers, Switches, Hubs, Firewalls, Modems etc.
These devices, ranging from humble routers to advanced switches, form the backbone of any computer network, playing a pivotal role in ensuring efficient communication.
Think of the internet like a highway for information. Network devices are the unseen workers like traffic controllers and bridge builders, making sure messages (data packets) get where they need to go smoothly and safely. They keep things moving fast and protect the messages along the way..!
Diving deeper into Routers: The Traffic Directors of the Network
Routers are more than just simple traffic directors; they're like intelligent switchboard operators navigating a complex web of information highways. Here's how they function in-depth:
1. Packet Forwarding: When you send an email or browse a website, your device breaks down the information into smaller packets. Routers analyze the destination address (IP address) in each packet and use a "routing table" to determine the best path for that packet to travel. This table is like a map highlighting efficient routes based on factors like network congestion and distance.
2. Pathfinding Algorithms: Routers employ sophisticated algorithms to choose the optimal path. Popular ones include the Dijkstra's algorithm, which finds the shortest path, and the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), which considers factors like congestion and bandwidth availability.
3. Addressing Different Networks: Routers act as bridges between different networks, like your home network and the wider internet. They understand different addressing schemes (like IP addresses) and translate them accordingly, ensuring smooth communication across diverse networks.
4. Firewall and Security: Many routers include built-in firewall functionalities, acting as guardians against malicious traffic. They filter incoming and outgoing data based on pre-defined rules, protecting your network from unauthorized access and harmful attacks.
5. Advanced Features: Modern routers offer various advanced features like:
- Dual-band Wi-Fi: Supports both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies, catering to different connection needs and speeds.
- Mesh Networking: Creates a seamless Wi-Fi experience across your entire home by using multiple interconnected routers.
- Quality of Service (QoS): Prioritizes specific types of traffic (e.g., gaming, video streaming) for better performance.
- Guest Network: Offers a separate, temporary Wi-Fi connection for visitors without access to your main network.
Understanding routers goes beyond just knowing they direct traffic. They're essential components ensuring efficient, secure, and reliable data flow in our interconnected world.
The Switches: The Smart Connectors of Your Network
While routers handle inter-network traffic, switches excel within a single network, like your home or office. Imagine them as smart mailboxes efficiently sorting and delivering letters (data packets) to their intended recipients (devices).
1. Targeted Delivery: Unlike routers, switches don't need to decipher complex internet destinations. They identify devices within the network by their unique "hardware addresses" (MAC addresses). When a device sends data, the switch reads the MAC address in the packet and forwards it only to the intended recipient, not everyone on the network.
2. Minimizing Traffic Jams: This targeted approach significantly reduces "collisions" and congestion on the network. Imagine if every house received every piece of mail delivered to your street! Switches prevent this chaos, resulting in faster and smoother data flow for everyone.3. Enhanced Performance: By ensuring data reaches its intended destination quickly and directly, switches contribute to a noticeable performance boost. Think of it like switching from a single-lane country road to a multi-lane highway – more devices can send and receive data without getting stuck in traffic.
4. Intelligent Features: Modern switches go beyond basic switching, offering:
- VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks): Create logical subdivisions within a network for better organization and security.
- Quality of Service (QoS): Prioritize specific data types (e.g., video conferencing) for optimal performance.
- Multi-gigabit speeds: Support high-bandwidth applications like HD streaming and online gaming.
Switches are crucial components for creating a fast, efficient, and secure network within your local environment. They ensure only the right data reaches the right devices, optimizing performance and keeping your network running smoothly.
Hubs: The History and Limitations of Network Connectors
Think of hubs as the original network connectors, similar to basic power strips plugging multiple devices into the same outlet. While they served a purpose in the past, their limitations haven't kept pace with modern network demands.
1. Broadcasting, Not Targeting: Unlike switches, which direct data to specific devices, hubs send all data received to every connected device. Imagine everyone on the same street receiving the same mail, regardless of the addressee. This "broadcasting" leads to:
- Congestion: All devices receive unnecessary data, overloading the network and slowing everything down.
- Collisions: When multiple devices transmit simultaneously, their signals collide, corrupting data and further reducing efficiency.
2. Simpler, But Outdated: While hubs are easy to set up and manage, their lack of intelligence limits their effectiveness in modern networks. Switches offer significant performance and security advantages, making them the preferred choice for efficient data flow.
3. Historical Significance: Although not widely used today, hubs played a critical role in the early development of networks. They allowed basic connectivity and paved the way for more advanced networking technologies.
Understanding the limitations of hubs helps us appreciate the advancements offered by modern switches and routers, ensuring efficient and secure communication in our interconnected world.
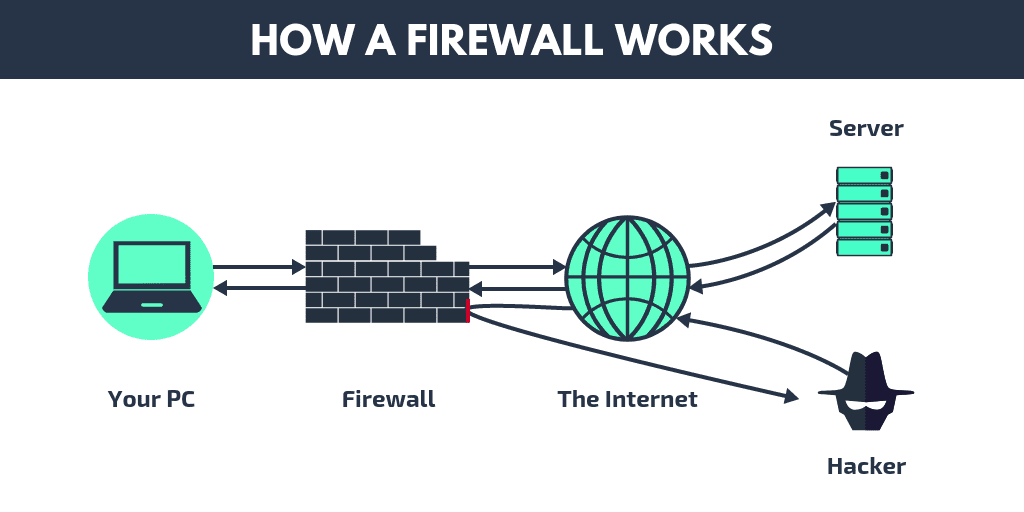
Firewalls: The Vigilant Guardians of Your Digital Castle
Imagine your network as a castle and firewalls as its loyal guards. Like vigilant sentries, they continuously scan incoming and outgoing traffic, ensuring only authorized visitors with proper permits (data packets) enter and leave.
1. Gatekeepers with Rules: Firewalls don't blindly accept everything. They operate based on pre-defined rules, carefully examining each data packet's origin, destination, and content. Think of these rules as the guards' instructions – if a packet doesn't meet the criteria, it gets blocked at the gate.
2. Shields Against Malicious Intent: Malicious software, hackers, and other digital threats constantly try to infiltrate networks. Firewalls act as shields, blocking suspicious traffic and preventing unauthorized access. They're like the guards stopping unwanted visitors and protecting the castle from harm.
3. Different Types of Firewalls: Just like castles have different defenses, firewalls come in various flavors. Hardware firewalls are dedicated devices, while software firewalls live on individual computers. There are also firewalls built into routers, offering an additional layer of protection.
4. Constant Vigilance: The digital world is ever-evolving, and so are the threats. Firewalls require regular updates and monitoring to stay effective against ever-sophisticated attacks. Think of the guards constantly training and adapting to new tactics to ensure the castle's safety.
5. Not Impenetrable Fortresses: While firewalls are crucial, they're not foolproof. It's essential to combine them with other security measures like strong passwords and user awareness to build a strong defense against cyber threats. Remember, even the most vigilant guards can't prevent every breach, so layered security is key.
By understanding how firewalls work, we can appreciate their vital role in protecting our valuable data and fostering a secure digital environment.
Modems: The Interpreters of the Digital Age
Think of modems as translators bridging the gap between the digital language of computers and the analog world of cables and wires. While the concept remains the same, modern modems have evolved tremendously to keep pace with our ever-growing demands.
1. Beyond Traditional Dial-Up: The days of screeching dial-up connections are thankfully behind us. Today's modems support a variety of high-speed technologies like:
- Cable: Utilizes cable TV infrastructure for fast and reliable internet access.
- DSL: Leverages existing phone lines for faster speeds compared to dial-up.
- Fiber Optic: Transmits data using light pulses, offering incredibly high speeds and low latency.
- Cellular: Provides internet access through mobile networks, enabling connectivity on the go.
2. Integration and Convenience: Many modern modems come integrated with routers, creating a single device for both internet access and Wi-Fi distribution. This simplifies setup and reduces clutter.
3. Advanced Features: Some modems offer advanced features like:
- Multiple Wi-Fi bands: Support for both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies for better compatibility and performance.
- Guest Wi-Fi: Offers a separate, temporary network for visitors without accessing your main network.
- Parental controls: Manage internet access and filter content for specific devices.
4. Future-Proofing: Choosing a modem compatible with the latest standards like DOCSIS 3.1 (cable) or VDSL2 (DSL) can ensure you're prepared for future speed upgrades without needing to replace your hardware.
5. Choosing the Right Modem: With various options available, it's crucial to consider your internet service provider, desired speed, budget, and desired features when selecting a modem.
Modern modems are essential components in our digital lives, seamlessly connecting us to the vast world of information. By understanding their role and advancements, we can make informed choices to optimize our internet experience.













0 Comments